WHAT IS A RESISTOR?
A resistor is an electrical component that limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in an electronic circuit and can be used to provide a specific voltage for an active device. The higher the resistance of the resistor the smaller the current flows. A resistor look like this :-

HOW DOES RESISTOR REGULATE CURRENT?
If you connect a LED directly to a 9V battery, LED gets damaged and no longer works. But if you connect a resistor between the positive terminal of battery and LED, LED glows without damaging it. This shows us that the resistor regulate current flowing through it.
WHAT IS OHM (Ω)?
The ohm (Ω) is the SI unit of electrical resistance. An ohm is equivalent to a volt per ampere.
CONVERSION
1 mΩ = 10−3 Ω
1 kΩ = 103 Ω
1 MΩ = 106 Ω
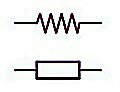
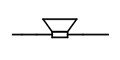
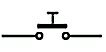
SYMBOL FOR RESISTOR
Both symbols below are used to represent resistor in a circuit diagram. You can use any one of the two symbols.

CONNECTING RESISTOR
A resistor is a two-terminal electrical component like the one below

Resistor can be connected either way, that means it have no positive and negative terminal.
WHAT IS RESISTANCE?
The definition of resistance is based upon the Ohm’s law given by the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm. The Ohm’s Law states that the voltage [V] across a resistor is directly proportional to the current [I] flowing through it. Here, its resistance [R] is the constant of proportionality. Therefore,
V = I * R