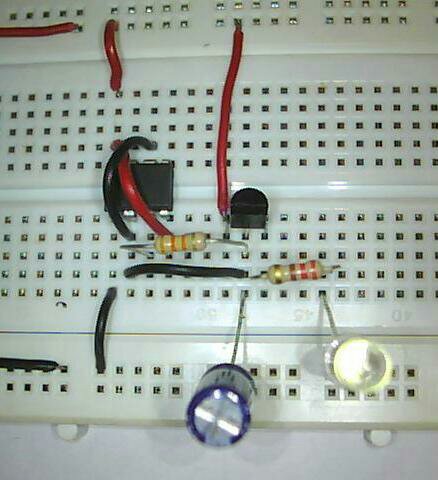
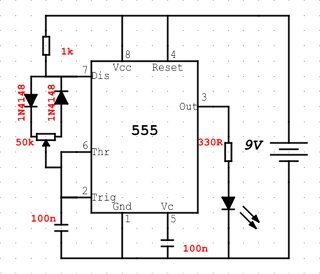
The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. The 555 can be used to provide time delays, as an oscillator, and as a flip-flop element. The primary purpose of the 555 timer is the generation of accurately timed single pulse or oscillatory pulse waveforms. The 555 has three main operating modes Monostable, Astable, and Bistable. Each mode represents a different type of circuit that has a particular output. I will make a post on the 555 main three operating modes later.
THE FUNCTION OF EACH PINS
Pin 1 Ground [GND] – Most negative supply connected to the device, normally this is common ground (0V).
Pin 2 Trigger [TRIG] – Detects 1/3 of rail voltage to make output HIGH.
Pin 3 Output [OUT] – The 555 timer output signal pin.
Pin 4 Reset [RES] – reset. Must be taken below 0.8v to reset the chip
Pin 5 Control [CON] – A voltage applied to this pin will vary the timing of the RC network
Pin 6 Threshold [THRESH] – Detects 2/3 of rail voltage to make output LOW only if pin 2 is HIGH
Pin 7 Discharge [DIS] – Goes LOW when pin 6 detects 2/3 rail voltage but pin 2 must be HIGH.
Pin 8 VCC [VCC] – Most positive supply connected to device, normally this is 5V, 10V or 15V.
555 IC PINOUT
To identify the Pin1, place the 555 on a flat surface such a way that the small circle is in the top left corner.Now identification of pins are easy. Now start from the top left corner (where the small circle is) first pin is pin1, next pin below is pin2, next pin below is pin3, next pin below is pin4, pin5 is on the bottom right corner, next pin above is pin6, next pin above is pin7, next pin above is pin8.
To identify the pins of IC start from the top left corner where the small circle is and the top first pin will be pin1 and start counting in the pins in anticlockwise direction pin 2, pin 3, pin 4….and stop at the first pin on the top right corner which in the case of 555 is pin 8.
Here I have marked the 8 pins on a 555 iC:-

For the easy understanding of the circuit we always draw the 555 as a building block, as shown below with the pins in the following locations. I have given functions of each pin next to it. So you can remember it easily. I hope you can understand it.

If you have doubt in identify the pins of 555 IC OR function of each pin, put it in the comments and I will help you to solve it.