Diode is a two-terminal electronic component with asymmetric conductance , it has low (ideally zero) resistance to current flow in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other. Today most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconductors such as selenium or germanium are sometimes used. A semiconductor diode, the most common type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals.
FUNCTIONS
The most common function of a diode is to allow an electric current to pass in one direction (called the diode’s forward direction), while blocking current
in the opposite direction (the reverse direction). This unidirectional behavior is called rectification, and is used to convert alternating current to direct current, including extraction of modulation from radio signals in radio receivers—these diodes are forms of rectifiers .
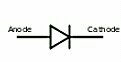
Symbol of diode
CONNECTING DIODE PROPERLY
I hope you understand the positive and negative terminal of diode.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF DIODES
There are different types of diodes and each of them have different function.
Zener diodes are used to regulate voltage.
avalanche diodes are used to protect circuits from high voltage surges.
varactor diodes are used to electronically tune radio and TV receivers.
tunnel diodes , Gunn diodes, IMPATT diodes are used to generate radio frequency
oscillations.
light emitting diodes(LED) are used to produce light.
We will be using LEDs and photodiode or LDR in our projects, so here is the note on two. To know more about LED check out my Light Emitting Diode (LED) post or Connecting LED Properly post, to know more about LDR click here
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
In a diode formed from a direct band-gap semiconductor, such as gallium arsenide, carriers that cross the junction emit photons when they recombine with the majority carrier on the other side. Depending on the material, wavelengths (or colors) from the infrared to the near ultraviolet may be produced. The forward potential of these diodes depends on the wavelength of the emitted photons: 2.1 V corresponds to red, 4.0 V to violet. The first LEDs were red and yellow, and higher- frequency diodes have been developed over time. All LEDs produce incoherent, narrow- spectrum light; “white” LEDs are actually combinations of three LEDs of a different color, or a blue LED with a yellow scintillator coating. LEDs can also be used as low-efficiency photodiodes in signal applications. An LED may be paired with a photodiode or phototransistor in the same package, to form an opto- isolator .
Photodiodes
All semiconductors are subject to optical charge carrier generation. This is typically an undesired effect, so most semiconductors are packaged in light blocking material.
Photodiodes are intended to sense light( photodetector ), so they are packaged in materials that allow light to pass, and are usually PIN (the kind of diode most sensitive to light). A photodiode can be used in solar cells , in photometry, or in optical communications . Multiple photodiodes may be packaged in a single device
Most popular 1N-series diodes
We will be using 1N-series diodes. The standardized 1N-series numbering EIA370 system was introduced in the US by EIA/JEDEC (Joint Electron Device Engineering Council) about 1960. Among the most popular in this series were:
1N34A/1N270 (Germanium signal),
1N914/1N4148 (Silicon signal),
1N4001 -1N4007 (Silicon 1A power rectifier) and
1N54xx (Silicon 3A power rectifier)
If you want to know more about diode let me know it through the comments.